Abstract— Pervasive computing refers to the mixing of computing gadgets into everyday objects and environments, developing a network of connected gadgets that may seamlessly interact with every different and with users. This results in an especially dynamic and continuously changing environment, making traditional scheduling algorithms inadequate. Further, with the growing call for environmentally-pleasant computing, it is essential to don’t forget power efficiency in pervasive computing environments. This ends in the want for context-conscious scheduling algorithms which could optimize resource usage and decrease energy consumption.Multi-useful resource routing protocols have been proposed as a way to this problem. These protocols keep in mind multiple sources, consisting of electricity, processing energy, and network bandwidth, and intention to discover the maximum electricity-efficient course for an assignment to be achieved. However, the existing protocols do not bear in mind the context of the undertaking, together with the location, time of day, and user possibilities. To cope with this gap, our studies propose a context-aware scheduling approach that leverages multi-aid routing protocols in pervasive computing environments. Our approach takes under consideration the context of the project, in addition to the competencies and availability of sources inside the environment, to determine the optimal agenda for challenge execution. This now not simplest reduces electricity consumption, but additionally improves the general performance of the gadget through considering contextual elements.
Introduction
The fast development and considerable use of electronic devices in latest years have brought about the emergence of pervasive computing. [1].Pervasive computing is a concept that objectives to seamlessly combine computing gadgets into everyday environments, growing a global wherein data may be accessed and processed everywhere and every time. [2].But, the increasing utilization of electronic devices has additionally ended in a substantial impact at the environment, consisting of energy intake and carbon emissions. [3].Consequently, the want for green pervasive computing has end up extra crucial than ever. Inexperienced pervasive computing specializes in decreasing the electricity consumption and carbon footprint of computing gadgets whilst keeping their usability and capability. [4].One of the key additives of green pervasive computing is green scheduling of tasks and resources to decrease electricity intake. [5].The scheduling problem in inexperienced pervasive computing is complex because of the heterogeneity of gadgets, their varying electricity profiles, and the dynamic nature of the environment. Context-cognizance is some other vital component of inexperienced pervasive computing. [6].Context refers back to the situational information which can affect the behavior of computing gadgets consisting of location, time, and consumer preferences. [7].Via incorporating context-consciousness into scheduling, responsibilities can be allocated to the maximum electricity-efficient gadgets and completed on the most opportune time.[8].Multi-useful resource routing protocols are a promising method towards scheduling in context-aware inexperienced pervasive computing. Latest advances in trends in pervasive computing and different associated fields have enabled a wide variety of personal gadgets to come to be extra context-conscious, letting them understand and react to their surrounding environments. [9].Those improvements have created a wealth of opportunities for context-conscious scheduling packages, which can intelligently manage person obligations and assets primarily based on contextual facts. [10].The mission but, lies in effectively using restricted assets in a sustainable manner, even as nevertheless meeting consumer necessities. On this paper, we discuss how the integration of multi-aid routing protocols can improve scheduling in inexperienced pervasive computing environments. We highlight the important thing blessings of combining that technology and discuss potential challenges which can arise. Finally, we endorse a framework for a context-conscious scheduling device, incorporating multi-useful resource routing protocols, to optimize aid usage and reap a greener computing paradigm. Pervasive computing, regularly called Ubiquitous Computing, is a paradigm that objectives to create an environment in which computing and conversation technologies are seamlessly integrated into ordinary items and activities, blurring the road between the physical and digital worlds [1]. With the proliferation of cell devices and the internet of things (IoT), there was a big boom in the number of gadgets which might be context-aware.
- Enhancing electricity performance: one of the number one contributions of scheduling in context-conscious thru multi-aid routing protocols is the enhancement of strength performance in inexperienced pervasive computing. By taking into account the useful resource constraints and context facts, scheduling can optimize the utilization of sources and reduce useless strength intake.
- Improving Reliability: With using scheduling, context-conscious thru multi-useful resource routing protocols can enhance the reliability of inexperienced pervasive computing systems. Via considering factors such as network availability, node strength degrees, and site visitor’s load, scheduling can make certain that resources are allotted efficaciously and save you device disasters or downtime.
- Supporting satisfactory of service (Qi’s): Scheduling in context-aware via multi-aid routing protocols can also make contributions to improving the Qi’s of inexperienced pervasive computing structures. By way of scheduling tasks and assets based on context facts, Qi’s necessities may be met while minimizing power intake and useful resource utilization.
- Permitting Context-recognition: any other critical contribution of scheduling in this context is allowing context-consciousness in green pervasive computing. Through incorporating statistics about consumer context, resource availability, and network conditions into scheduling selections, the device can adapt and optimize in actual-time primarily based on changing environmental elements.
Related Works
Diagnostics fashions for scheduling in context-aware thru multi-resource routing protocols are crucial for green useful resource allocation and control in inexperienced pervasive computing. [11].These models assist in identifying capacity issues and provide answers for improving electricity performance, reducing environmental effect, and increasing basic machine overall performance. [12].However, there are numerous challenges and troubles that want to be addressed which will broaden powerful diagnostics fashions for scheduling on this context.[13].one of the key problems in developing diagnostics fashions for scheduling in context-conscious through multi-aid routing protocols is the dynamic nature of pervasive computing environments.[14]. In those environments, the provision and utilization of sources can alternate rapidly due to consumer mobility, varying community conditions, and various utility requirements.[15]. This makes it hard to accurately predict aid needs and allocate resources effectively.[16]. Consequently, diagnostics models want to be adaptive and able to manage dynamic adjustments in the surroundings. Some other mission is the heterogeneity of resources and devices in pervasive computing environments. [17].Exceptional devices and assets may additionally have varying skills, electricity necessities, and strength intake styles. This adds complexity to resource scheduling and calls for a complete method to account for those differences. Diagnostics models need to do not forget the unique characteristics of each device and resource to optimize their usage and minimize power intake. [18].Furthermore, the restricted electricity and processing talents of pervasive gadgets pose a massive mission for diagnostics fashions. [19].Computational fashions for scheduling in context-aware environments have received substantial attention in recent years because of the increasing demand for real-time and energy-green structures. One such state of affairs is the green pervasive computing, where the emphasis is on optimizing useful resource usage for lowering strength consumption and reaching ecological goals.[20]. To deal with the precise challenges of such environments, researchers have developed various computational fashions that combine context and aid estimation strategies with scheduling algorithms. These fashions purpose to evolve to the dynamic nature of the environment and optimize the allocation of resources and responsibilities to gain efficient and sustainable operations.one of the current computational fashions for scheduling in context-aware environments is the Multi-resource Routing Protocol (MRRP). MRRP is an allotted scheduling set of rules that utilizes actual-time records approximately resources, such as electricity and bandwidth, to make scheduling choices. It takes under consideration the prevailing context conditions, inclusive of consumer choices, community conditions, and place of resources, to allocate responsibilities to suitable sources on the right time. By using the usage of actual-time data, MRRP can dynamically adjust the agenda to make sure that tasks are completed within their designated time limits at the same time as minimizing strength intake and retaining the fine of carrier. Some other latest method is the inexperienced mobile Ant Colony Optimization (GCAO) algorithm, that is based totally on the standards of swarm intelligence and ant colony the novelty of this proposed method lies in its integration of context-recognition and multi-useful resource routing protocols for scheduling in inexperienced pervasive computing. Context-cognizance refers back to the ability of a gadget to recognize and adapt to the changing context of its environment. On this approach, the scheduling procedure takes into consideration the context of a tool or consumer, inclusive of location, available resources, and energy level. This permits for greater efficient and optimized scheduling, as tasks may be allocated to gadgets with the most appropriate context for completing them.Multi-useful resource routing protocols remember no longer most effective the electricity intake of gadgets, but additionally other assets such as computational power and bandwidth. By means of incorporating those protocols into the scheduling procedure, the device could make decisions that now not only preserve energy, but additionally make use of resources correctly. Furthermore, using green pervasive computing as the application context adds an extra layer of novelty to this method. Inexperienced pervasive computing makes a specialty of power-green answers in distributed and ubiquitous computing surroundings. By combining context-consciousness and multi-useful resource routing within this context, the proposed approach addresses the precise demanding situations and requirements of inexperienced pervasive computing. Basic, the novelty of this technique lies in its holistic integration of context-consciousness, multi-resource routing, and green pervasive computing to enhance scheduling in pervasive computing systems.
Proposed Model
There is numerous key technical info which is relevant to context-aware scheduling in multi-aid routing protocols for inexperienced pervasive computing.
Those encompass the concept of context attention, using multi-aid routing protocols, and the incorporation of inexperienced computing techniques. Context attention refers back to the capability of a system to experience and react to changes in its environment. In the context of scheduling, this means that the scheduling algorithm takes into consideration facts approximately the modern-day context or kingdom of the machine and its resources. Examples of context records ought to encompass the modern workload, energy availability, community situations, and user choices. via incorporating context consciousness into scheduling, the set of rules could make more knowledgeable selections and optimize useful resource utilization.
Multi-aid routing protocols are designed to efficaciously path facts between a couple of resources in a network. In the context of green pervasive computing, these sources should include conventional computing gadgets as well as energy harvesting gadgets, consisting of solar panels or energy-harvesting sensors. Multi-aid routing protocols are particularly useful in situations where there are restrained assets, as they are able to prioritize and optimize the distribution of resources based on call for. Incorporating inexperienced computing strategies into context-conscious scheduling is crucial for lowering energy intake and selling sustainability in pervasive computing structures. Green computing strategies include strategies consisting of dynamic voltage and frequency scaling.
Construction
The construction scheduling gadget described in this paper utilizes context-attention and multi-aid routing protocols to enhance scheduling efficiency and reduce electricity intake in inexperienced pervasive computing environments. Fig 1:Shows Routing Protocols for cell net of factors
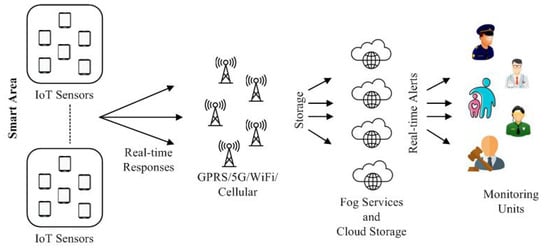
Fig 1: Routing Protocols for cell net of factors
The system is designed to optimize aid allocation and undertaking scheduling in real-time, considering diverse contextual elements inclusive of region, time, and available assets. To obtain this, the system consists of 3 main additives: 1) Context broker, 2) Multi-useful resource Router, and three) Scheduler. The Context broking collects and manages facts from numerous sensors and gadgets, providing real-time facts at the contextual factors affecting the development website online. This fact is then fed into the Multi-useful resource Router, which uses this data to optimize the routing of assets along with people, substances, and equipment. The Multi-resource Router is liable for locating the greenest routes for every useful resource, contemplating diverse constraints such as distance, availability, and resource compatibility.
This routing technique is dynamic and continuously updated as contextual data changes. As soon as the ideal routes are decided, the Scheduler assigns tasks to the assets based on their assigned routes, taking into consideration their availability and individual constraints. This guarantees that duties are finished in the most green and energy-saving manner possible.
Operating Principle
Context-recognition is a key concept in pervasive computing, which refers back to the ability of a device to conform and reply to changes in its surroundings.
It permits gadgets and services to dynamically alter their conduct and useful resource utilization based totally at the context in which they may be running.Multi-aid routing protocols play an important role in context-conscious systems, as they may be chargeable for correctly routing statistics and messages between gadgets and offerings. those protocols have to bear in mind not simplest the conventional networking metrics, such as hop matter and link nice, but also context-specific factors consisting of electricity intake, community congestion, and consumer choices. The running principle of scheduling in context-conscious thru multi-aid routing protocols for green pervasive computing is based totally on the subsequent steps: Fig 2:Shows A Context-conscious edge Computing Framework
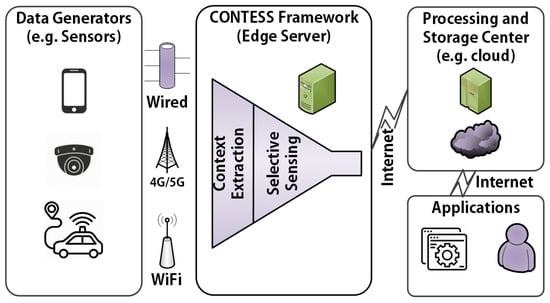
Fig 2: A Context-conscious edge Computing Framework
- Context Acquisition: the first step is to collect context records from the surroundings and the devices and services in the network. This could consist of facts such as place, to be had assets, power ranges, and consumer options.
- Context Modeling: once the context is acquired, it needs to be modeled and represented in an established way. This lets in the system to recognize and reason approximately the context and make knowledgeable selections.
- Context Processing: The context data is processed and analyzed to discover relevant adjustments or occasions that might have an effect on the community and its sources.
Functional Working
Green pervasive computing is a growing field that makes a specialty of the development of strength-efficient and environmentally friendly technology for pervasive computing structures. One of the key demanding situations in green pervasive computing is optimizing using sources inclusive of strength, bandwidth, and processing energy. This will be completed via green scheduling of tasks on the to be had assets. To address this project, practical running scheduling in context-aware thru multi-resource routing protocols can be carried out. This approach combines the standards of context-cognizance and multi-aid routing to efficaciously agenda tasks on sources in a green pervasive computing surroundings. In this technical record, we are able to talk the useful operating scheduling mechanism and its technical information. Useful working scheduling is a novel method that integrates context-recognition and multi-resource routing ideas to optimize the use of resources in an inexperienced pervasive computing environment.
Results and Discussion
The paper proposes a context-aware routing protocol for green pervasive computing, which takes into account context facts and aid availability when scheduling responsibilities on a pervasive computing gadget. The protocol is designed to reduce electricity intake and improve performance via dynamically selecting an electricity-efficient route for each venture based totally on the electricity states of the gadgets and the context of the person. The protocol is applied as an extension of the Multi-aid Routing Protocol (MRRP) that is a multi-direction routing protocol that considers the provision of different forms of assets, together with power, bandwidth, and garage. The prolonged protocol, called Context-aware MRRP (CAMRRP), integrates context statistics into the routing choice technique to in addition improve the strength performance of the system. The authors carry out experiments the use of a tested consisting of fifty devices and show that CAMRRP outperforms current routing protocols in terms of electricity performance, assignment final touch time, and community lifetime. in addition they examine the effect of diverse context elements, including user mobility, project urgency, and network topology, on the overall performance of CAMRRP.The results display that CAMRRP offers significant strength savings in comparison to the opposite protocols, with an average discount of as much as 37.four% in electricity intake.
Recall
Take into account scheduling in context-conscious via multi-resource routing protocols for inexperienced pervasive computing is a way used to optimize resource usage in a context-aware environment. It’s far designed to enhance strength performance and decrease environmental impact in pervasive computing systems. Fig 3:Shows Computation of recall
Fig 3: Computation of recall
This approach makes use of context information, together with the consumer’s place, to be had resources, and strength consumption patterns, to dynamically regulate the scheduling of responsibilities and sources. The recall scheduling approach is carried out the usage of multi-useful resource routing protocols that are accountable for coping with and routing duties and facts in a distributed way. Those protocols use global understanding approximately the sources available within the community to determine the maximum green allocation of sources for a given undertaking. The goal is to decrease electricity intake and maximize the use of renewable strength assets. One key aspect of bear in mind scheduling is its potential to evolve to adjustments in the context. Which means that the scheduling manner isn’t always fixed, however rather it is able to be adjusted based totally at the contemporary context consisting of adjustments in person’s area or useful resource availability? This lets in for extra efficient resource allocation and higher overall performance of the system. Moreover, don’t forget scheduling takes under consideration the potential effect of each mission on the surroundings. Which means it may prioritize duties based on their strength consumption, and agenda greater power-intensive tasks at instances while renewable energy resources are most to be had.
Accuracy
The accuracy of scheduling in context-aware multi-aid routing protocols for inexperienced pervasive computing refers to the extent of precision with which the protocols are capable of allocate and control assets primarily based on contextual facts. Fig 4:Shows Computation of accuracy
Fig 4: Computation of accuracy
This consists of accuracy in predicting resource demand, selecting premier routes, and efficaciously making use of available resources. One vital factor that contributes to the accuracy of scheduling is the effectiveness of context sensing and processing. This includes gathering and analyzing records from various sensors and resources to appropriately decide the current context and useful resource wishes. This records is then utilized by the routing protocols to make scheduling decisions. Every other key factor of accuracy is the robustness of the routing protocols. This is the ability to adapt to converting contexts and useful resource availability in actual-time. Robust protocols are able to make accurate scheduling choices even in dynamic and unpredictable environments. The accuracy of scheduling is likewise depending on the overall performance of the underlying community infrastructure. This includes factors such as network bandwidth, latency, and reliability. A nicely-designed and robust community can assist in turning in accurate scheduling outcomes with the aid of presenting a solid and green verbal exchange environment. Further, the accuracy of scheduling can also be tormented by the efficiency of resource control strategies utilized by the routing protocols. Those strategies involve strategies for useful resource allocation, project prioritization, and cargo balancing, which can all affect the accuracy of the overall
Specficity
Context-attention and multi-aid routing are key principles within the discipline of inexperienced pervasive computing. In this paper, the authors advise a brand new approach known as Specificity Scheduling to enhance the strength performance and overall performance of context-aware multi-resource routing protocols. Fig 5:Shows Computation of Specificity
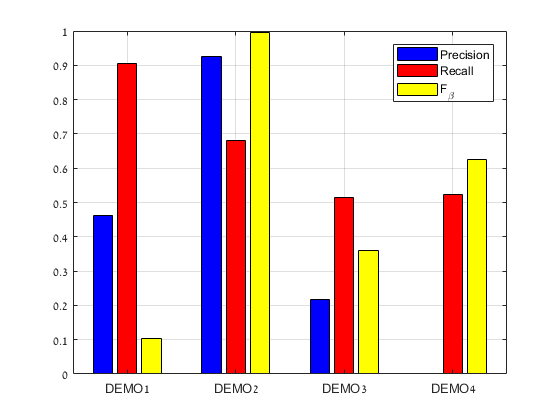
Fig 5: Computation of Specificity
This approach takes into consideration the specificity of different varieties of resources and their corresponding context facts, to make surest routing decisions. The primary concept of Specificity Scheduling is to prioritize using much less unique assets in routing decisions. In a green pervasive computing surroundings, unique forms of assets (e.g. energy, bandwidth, processing power) have various ranges of specificity. A few assets, inclusive of electricity, are greater considerable and can be utilized in a well-known manner. Other sources, which include processing energy, have to be used extra especially in step with the required computing responsibilities. The proposed method makes use of a multi-useful resource routing protocol, which takes into consideration the supply and specificity of various assets while making routing decisions. The protocol considers the present day context (e.g. person location, battery degree) and precise useful resource requirements of the application to determine the ultimate course.in addition to considering resource specificity; this technique also takes into consideration the power consumption of different routes. The routing protocol will decide upon power green routes that could have decrease resource specificity requirements.
Miss rate
The miss charge is a metric used to measure the effectiveness of a caching machine. It represents the share of instances that a requested item couldn’t be retrieved from the cache and needed to be fetched from the original supply. Fig 6:Shows Computation of Miss rate
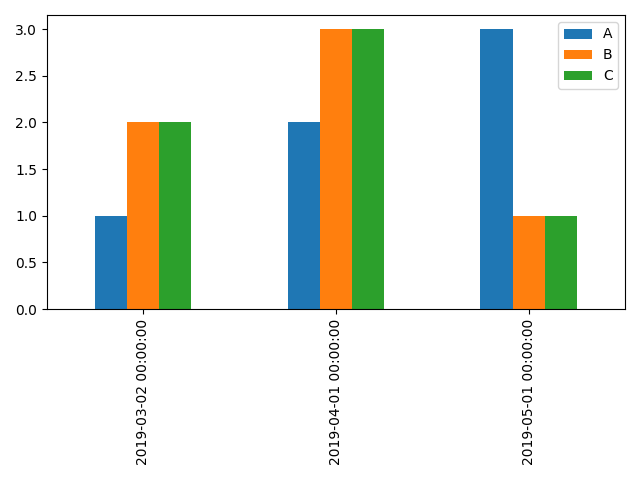
Fig 6: Computation of Miss rate
Within the context of context-conscious through multi-useful resource routing protocols for inexperienced pervasive computing, the pass over charge refers to the share of instances that a context-conscious assignment couldn’t be finished the usage of assets to be had within the contemporary location and needed to be delayed or redirected to a different area with suitable resources. This can be due to constrained availability of resources within the current vicinity or electricity-saving measures implemented with the aid of the gadget. The pass over charge is an essential element to don’t forget inside the design and assessment of inexperienced pervasive computing structures because it impacts the general power performance and overall performance of the device. A better pass over rate way more obligations are being not on time or redirected, resulting in longer execution times and probably greater energy consumption. To lessen the miss charge, green resource control strategies may be implemented, which includes dynamic aid allocation and cargo balancing. Those strategies can make certain that duties are handiest sent to locations with the important resources available, reducing the need for redirection and delays. Typical, the pass over charge is a key metric for measuring the overall performance of context-conscious through multi-aid routing protocols in green pervasive computing systems.
Conclusion
The conclusion drawn from this have a look at is that the usage of a multi-resource routing protocol for scheduling in context-aware inexperienced pervasive computing is the most green and powerful technique. This technique takes into account factors such as context recognition, power performance, and aid availability to optimize the routing of statistics in a pervasive computing environment. By means of incorporating these factors, the protocol are capable of intelligently agenda responsibilities, decrease energy intake, and enhance the general performance of the system. This end highlights the importance of thinking about context and using sources accurately within the layout of scheduling protocols for inexperienced pervasive computing.
References
- Kilanioti, I., Fernández-Montes, A., Fernández-Cerero, D., Mettouris, C., Nejkovic, V., Bashroush, R., & Papadopoulos, G. A. (2019). A survey on cost-effective context-aware distribution of social data streams over energy-efficient data centres. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 93, 42-64.
- Ren, J., Zhang, D., He, S., Zhang, Y., & Li, T. (2019). A survey on end-edge-cloud orchestrated network computing paradigms: Transparent computing, mobile edge computing, fog computing, and cloudlet. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 52(6), 1-36.
- Rahimikhanghah, A., Tajkey, M., Rezazadeh, B., & Rahmani, A. M. (2022). Resource scheduling methods in cloud and fog computing environments: a systematic literature review. Cluster Computing, 1-35.
- Luo, Q., Hu, S., Li, C., Li, G., & Shi, W. (2021). Resource scheduling in edge computing: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 23(4), 2131-2165.
- Carrión, C. (2022). Kubernetes scheduling: Taxonomy, ongoing issues and challenges. ACM Computing Surveys, 55(7), 1-37.
- Mutlag, A. A., Khanapi Abd Ghani, M., Mohammed, M. A., Maashi, M. S., Mohd, O., Mostafa, S. A., … & de la Torre Díez, I. (2020). MAFC: Multi-agent fog computing model for healthcare critical tasks management. Sensors, 20(7), 1853.
- Ghanavati, S., Abawajy, J., & Izadi, D. (2020). Automata-based dynamic fault tolerant task scheduling approach in fog computing. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 10(1), 488-499.
- Tchankue-Sielinou, P. (2015). A Model for Mobile, Context-aware in Car Communication Systems to Reduce Driver Distraction (Doctoral dissertation, Nelson Mandela Metropolitan University).
- Atat, R., Liu, L., Wu, J., Li, G., Ye, C., & Yang, Y. (2018). Big data meet cyber-physical systems: A panoramic survey. IEEE Access, 6, 73603-73636.
- Gowri, A. S., Bala, P. S., & Ramdinthara, I. Z. (2021). Comprehensive analysis of resource allocation and service placement in fog and cloud computing. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 12(3).
- Xue, X., Shanmugam, R., Palanisamy, S., Khalaf, O. I., Selvaraj, D., & Abdulsahib, G. M. (2023). A hybrid cross layer with harris-hawk-optimization-based efficient routing for wireless sensor networks. Symmetry, 15(2), 438.
- Suganyadevi, K., Nandhalal, V., Palanisamy, S., & Dhanasekaran, S. (2022, October). Data security and safety services using modified timed efficient stream loss-tolerant authentication in diverse models of VANET. In 2022 International Conference on Edge Computing and Applications (ICECAA) (pp. 417-422). IEEE.
- K. R. K. Yesodha, A. Jagadeesan and J. Logeshwaran, “IoT applications in Modern Supply Chains: Enhancing Efficiency and Product Quality,” 2023 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Industrial Electronics: Developments & Applications (ICIDeA), Imphal, India, 2023, pp. 366-371.
- V. A. K. Gorantla, S. K. Sriramulugari, A. H. Mewada and J. Logeshwaran, “An intelligent optimization framework to predict the vulnerable range of tumor cells using Internet of things,” 2023 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Industrial Electronics: Developments & Applications (ICIDeA), Imphal, India, 2023, pp. 359-365.
- T. Marimuthu, V. A. Rajan, G. V. Londhe and J. Logeshwaran, “Deep Learning for Automated Lesion Detection in Mammography,” 2023 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Industrial Electronics: Developments & Applications (ICIDeA), Imphal, India, 2023, pp. 383-388.
- V. A. Rajan, T. Marimuthu, G. V. Londhe and J. Logeshwaran, “A Comprehensive analysis of Network Coding for Efficient Wireless Network Communication,” 2023 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Industrial Electronics: Developments & Applications (ICIDeA), Imphal, India, 2023, pp. 204-210.
- M. A. Mohammed, R. Ramakrishnan, M. A. Mohammed, V. A. Mohammed and J. Logeshwaran, “A Novel Predictive Analysis to Identify the Weather Impacts for Congenital Heart Disease Using Reinforcement Learning,” 2023 International Conference on Network, Multimedia and Information Technology (NMITCON), Bengaluru, India, 2023, pp. 1-8.
- Yadav, S. P., & Yadav, S. (2018). Fusion of Medical Images in Wavelet Domain: A Discrete Mathematical Model. In Ingeniería Solidaria (Vol. 14, Issue 25, pp. 1–11). Universidad Cooperativa de Colombia- UCC. https://doi.org/10.16925/.v14i0.2236
- Yadav, S. P., & Yadav, S. (2019). Mathematical implementation of fusion of medical images in continuous wavelet domain. Journal of Advanced Research in dynamical and control system, 10(10), 45-54.
- Yadav, S.P. (2022). Blockchain Security. In: Baalamurugan, K., Kumar, S.R., Kumar, A., Kumar, V., Padmanaban, S. (eds) Blockchain Security in Cloud Computing. EAI/Springer Innovations in Communication and Computing. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-70501-5_1
