Abstract— Aspect Computing is a decentralized computing paradigm that brings computation and facts garage towards the threshold of the community, in the direction of in which the records is being generated. It enables real-time statistics processing and analytics, reducing the latency and improving the reaction time. The emergence of latest aspect technologies has led to the adoption of block chain networks to facilitate comfy facts sharing in facet computing environments. Block chain era offers a decentralized and immutable ledger that permits at ease and transparent sharing of data among side devices.one of the essential challenges in facet computing is facts safety. With a large wide variety of gadgets connected to the threshold community, there’s a want for a at ease and efficient statistics sharing mechanism. Block chain offers a decentralized and tamper-proof answer for facts sharing, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of the shared records. By using leveraging features together with clever contracts, area gadgets can affirm and authorize records get entry to, making sure information privateers and security. Furthermore, block chain’s consensus mechanisms permit believe between special gadgets within the side community. This enables cozy records sharing and collaboration among devices owned by using distinct groups. for example, in a clever metropolis surroundings, where one-of-a-kind government businesses and personal agencies collect and technique facts, block chain can provide a comfy and decentralized platform for information sharing and collaboration.
Introduction
Block chain generation has emerged as a powerful tool for making sure comfortable and decentralized facts sharing in various industries. [1].Its ability in facet computing, a paradigm that brings computation and statistics garage closer to the devices and sensors at the brink of the network, has additionally gained considerable attention in current years. [2].Aspect computing has the ability to revolutionize records management, processing, and sharing by bringing the computation closer to the facts supply, reducing latency, and minimizing network congestion. [3].The mixing of block chain technology with aspect computing has the potential to unlock new opportunities for cozy and transparent facts sharing. here are a number of the viable packages of block chain in facet computing for at ease information sharing In conventional centralized records control structures, statistics is saved in a single location, making it susceptible to cyber-assaults and statistics breaches.[4]. With side computing, facts may be stored and processed toward the supply, decreasing the risk of records breaches. [5].Via combining block chain technology, which is based on disbursed ledgers, the information can be decentralized, disposing of the want for a central authority to manage and comfy the records. [6].This decentralized approach ensures that no single point of failure exists, making it tougher for hackers to compromise the statistics. [7].In current years, aspect computing and block chain era have emerged as two of the most promising technological innovations.[8]. Side computing, additionally referred to as fog computing, goals to system statistics at the edge of the network, closer to in which it’s far generated, in preference to sending it to a critical location for processing. [9].On the other hand, block chain is a decentralized virtual ledger that secures and information in an obvious and immutable way. [10].With the upward thrust of the net of factors (IoT) and the growing volume of information being generated, the combination of side computing and block chain has the potential to revolutionize the manner facts is processed and shared, enabling comfortable and green facts control. In this essay, we can explore the innovation of block chain programs in edge computing for cozy statistics sharing.one of the most important demanding situations inside the present day facts sharing panorama is the centralization of statistics in massive data centers, which poses sizeable protection dangers. Such centralized systems are susceptible to cyber-attacks, statistics breaches, and facts loss that may have intense results for people and corporations. Furthermore, the conventional facts sharing version is likewise luxurious and time-consuming, requiring a couple of intermediaries consisting of information aggregators, agents, and garage companies, to facilitate the records sharing system. This model additionally increases worries approximately information ownership and manage.
- Decentralization: Block chain era permits for decentralized data storage and processing, allowing cozy records sharing without the want for a centralized authority. This ensures that records isn’t always susceptible to an assault on a principal server or garage facility, and also gets rid of the threat of facts being managed or manipulated by way of a single entity.
- Records Integrity and Immutability: the use of block chain era ensures that facts shared within side computing networks stays secure and tamper-proof. Each transaction is recorded sequentially in blocks and is cryptographically linked to the previous block, making it in reality impossible for everyone to alternate or manage the records without leaving a trace.
- Comfy records Sharing: With block chain technology, records may be shared amongst a couple of participants in a comfy and obvious manner. using clever contracts permits for automatic and relaxed data sharing processes, making sure that records is most effective shared with legal events and can be accessed or used according to predefined policies and situations.
- Elevated efficiency and cost financial savings: by means of combining block chain technology with facet computing, businesses can gain increased efficiency and value financial savings. Facet computing permits for records to be processed and analyzed towards the factor of beginning, reducing the need for big statistics transfers and permitting faster choice making. this will result in value savings on facts garage and transfer, as well as progressed
Related Works
Block chain technology has been making great strides in numerous industries, with its disruptive capability to revolutionize strategies and facts dealing with. [11].But, the emergence of edge computing has delivered a layer of complexity to this already sophisticated technology. This has led to several challenges; specifically in diagnostic fashions for secure facts sharing in block chain applications.one of the primary troubles in diagnostics fashions for block chain programs in aspect computing is the alternate-off between safety and performance. [12].Area computing includes processing facts closer to the source, decreasing the need for centralization. However, this additionally method that touchy statistics is stored and processed on a dispensed community of gadgets, making it susceptible to malicious assaults. [13].In block chain, in which records is saved on an allotted ledger, this poses a sizable task in making sure statistics protection without compromising the performance of the gadget.[14]. Every other project with part computing in block chain programs is the shortage of standardization and interoperability. [15].In conventional centralized systems, a sure stage of standardization is hooked up, making it less complicated to integrate one of a kind programs and devices.[16]. But, area computing remains a particularly new concept, and there are no standardized protocols for communiqué and records sharing among devices. [17].This creates complexities in growing diagnostic fashions that can be carried out throughout specific side computing systems.
[18].In the cutting-edge virtual panorama, the appearance of edge computing has opened up a plethora of recent opportunities for records control and at ease statistics sharing. Part computing is a paradigm that enables records processing and storage to be finished at the edge of the community, toward wherein the statistics is being generated. [19].This technique permits for faster facts analysis and reduces the dependency on centralized cloud servers, main to advanced latency and community efficiency. But, with the growing adoption of part computing, the want for comfy data sharing has additionally come to be an essential situation. [20].In this context, block chain technology has emerged as a promising option to facilitate comfy statistics sharing in aspect computing environments. In current years, numerous computational fashions have been proposed to combine block chain with edge computing for cozy facts sharing. in this essay, we are able to discuss some of those models and their capacity applications in numerous domains.one of the important challenges in aspect computing is ensuring the safety and privacy of statistics, as information is no longer restrained to the relaxed partitions of a centralized cloud server. Any breach of security or unauthorized get admission to can lead to great results for people, companies, or even international locations. Block chain technology, with its decentralized and immutable nature, can provide trustless and comfy surroundings for statistics sharing. It may act as a disbursed ledger, recording and verifying the transactions the novelty of incorporating block chain generation in facet computing for at ease statistics sharing is multi-faceted and has numerous advantages. Some of the key incredible capabilities may be summarized as follows:
- Decentralized information storage: historically, information is saved on centralized servers, making it vulnerable to attacks and unmarried point of disasters. With block chain, information may be distributed and stored throughout more than one node, leading to enhanced protection and resilience in opposition to ability assaults.
- Enhanced information privateers: Block chain technology helps encryption through design, hence allowing secure sharing of sensitive data without revealing the real contents of the statistics. This lets in for improved privacy, facts safety, and consumer anonymity.
- Three. Smart Contracts for relaxed records sharing: Block chain technology lets in for the advent of clever contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement at once written into the code. Clever contracts allow secure and automatic information sharing between parties without the want for intermediary agree with.
- Improved statistics Integrity: Block chain’s distributed ledger generation lets in for tamper-proof storage of data and affords an immutable file of all transactions, making it tough for any birthday celebration to control or alter the shared records.
- Multiplied performance: With block chain, aspect computing can facilitate faster and greener processing as statistics can be shared instantaneously between gadgets.
Proposed Model
The time period “Block chain” refers to a disbursed digital ledger those statistics transactions in a secure and obvious way. It is often associated with crypto currencies; however its capacity uses go some distance beyond that. Block chain era is gaining recognition within the subject of aspect computing, which involves bringing computation and statistics storage in the direction of where it’s far needed, consisting of at the threshold of a network or on a user’s device.
The mixture of block chain and edge computing has the potential to revolutionize records sharing with the aid of providing comfy and decentralized storage, processing, and sharing of facts. This may be in particular beneficial for industries along with healthcare, supply chain management, and net of factors (IoT) gadgets. Under is the technical information about how block chain may be carried out in side computing for at ease records sharing: Block chain generation offers a decentralized garage answer in which facts is saved throughout multiple nodes in the network, rather than a primary server.
This guarantees that no unmarried point of failure can compromise the facts. In edge computing, this decentralized storage technique can be implemented with the aid of storing statistics on part devices, such as smartphones or IoT devices, in preference to an important server. This no longer handiest improves statistics protection but also reduces the weight on community bandwidth.
Construction
- Use of Block chain technology: the primary technical aspect of this application is the usage of block chain technology. Block chain is a decentralized allotted ledger technology that gives a tamper-proof and relaxed platform for records sharing. It eliminates the need for a central authority, making it best for facet computing environments in which a couple of events want to percentage information securely. Fig 1:Shows A block chain-based traceable and secure records-sharing scheme
![A blockchain-based traceable and secure data-sharing scheme [PeerJ]](https://sagevault.in/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/a-blockchain-based-traceable-and-secure-data-shari.png)
Fig 1: A block chain-based traceable and secure records-sharing scheme
- Smart Contracts: smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the phrases of the agreement among consumer and dealer being without delay written into lines of code. These contracts are then stored at the block chain, ensuring their validity and protection. Inside the context of edge computing, smart contracts may be used to automate the sharing of records among distinct gadgets and nodes, ensuring at ease and timely statistics exchange.
- Three. Edge nodes and gadgets: part computing involves using more than one node and devices connected to a local community for data processing and garage. These nodes and gadgets can be included into the block chain community the usage of virtual identities and cryptographic keys, making an allowance for at ease conversation and information sharing amongst them.
- Immutable and transparent document-maintaining: Block chain generation gives a tamper-proof and transparent record-maintaining machine. This makes it ideal for keeping song of data shared among devices in area computing environments. With block chain, all records transactions are recorded and time stamped, supplying an everlasting and immutable
Operating Principle
Running principle: The running principle of block chain generation in area computing for relaxed information sharing includes the usage of a decentralized ledger to save and manage data transactions among part devices.
This permits facts to be securely shared among facet gadgets without the want for a central authority. Fig 2:Shows area Computing integrated with Block chain
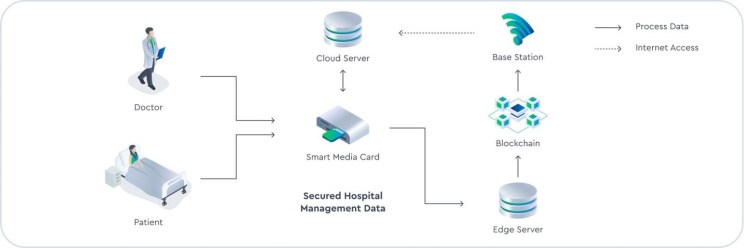
Fig 2: Area Computing integrated with Block chain
First, the brink devices accumulate and procedure information, that is then added to blocks within the block chain. Those blocks are cryptographically linked to previous blocks, developing an immutable chain of information. This ensures that any changes made to the facts in one block will be contemplated in all subsequent blocks, making it almost impossible to tamper with the facts. Subsequent, the edge gadgets use consensus algorithms to validate the statistics and reach a consensus on the order in which the blocks ought to be delivered to the block chain.
This ensures that everyone collaborating gadgets have the identical version of the block chain, stopping any discrepancies or malicious changes. Using public key cryptography additionally plays a critical position in the protection of the records. Every facet device has a completely unique pair of public and private keys, taking into consideration at ease authentication and encryption of information. This ensures that most effective legal gadgets can get entry to and percentage statistics. Whilst a records transfer is initiated among part devices, the transaction is demonstrated and brought to the block chain.
Functional Working
The block chain era, which was first delivered for crypto currency in Bit coin, has now won hobby from unique industries. With its precise capabilities such as decentralization, immutability, and transparency, block chain has the capacity to enhance numerous applications in side computing for comfortable information sharing. Aspect computing is a distributed system version that brings computation and facts storage in the direction of the region in which it is needed, lowering latency and increasing overall performance. By using leveraging the capabilities of facet computing, programs can manner and shop statistics closer to the supply, imparting higher response instances and decreasing the load on the relevant cloud infrastructure.
Block chain can be incorporated into aspect computing to offer a comfy and green platform for facts sharing. A few key technical factors of this integration are:
- Decentralized records garage: edge computing programs require a reliable and scalable data storage strategy to ensure records availability and accessibility. By leveraging block chain’s decentralized nature, statistics may be stored on multiple nodes, ensuring redundancy and fault tolerance. This additionally removes the want for a primary storage server, lowering the risk of an unmarried factor of failure.
- Clever contract-based statistics sharing: clever contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the settlement between purchaser and dealer being at once written into lines of code. They may be used in aspect computing to put in force records sharing agreements
Results and Discussion
Area computing has emerged as a promising era to conquer the demanding situations of centralized cloud computing for facts sharing in numerous application domains. It involves processing and garage of information in the direction of the source, thereby lowering community latency and improving response time. This enables an extensive variety of packages, which include internet of factors (IoT), smart towns, healthcare, automobile, and business internet, to collect, shop, and technique massive amounts of statistics in actual-time. But, information sharing in side computing environments introduces security concerns, as data is distributed throughout more than one device and facet nodes. This makes it at risk of cyber-assaults, facts leakage, and unauthorized get entry to. Block chain generation offers a promising method to address those security challenges by offering a comfy, disbursed and tamper-evidence statistics sharing mechanism.Blockchain is a decentralized ledger that data and shops data in a chain of blocks the usage of cryptographic techniques. In part computing, block chain can be utilized to comfy the records sharing technique by way of providing an immutable report of transactions among devices, facet nodes, and cloud servers.
Recall
Side computing has come to be a critical generation in latest years because of the boom of internet-linked gadgets and the demand for actual-time facts processing. Fig 1:Shows that Computation of Recall
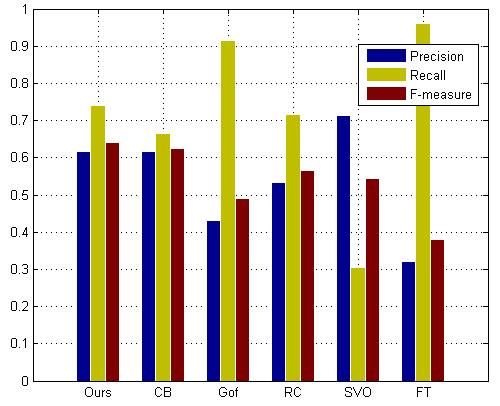
Fig 1: Computation of Recall
As more sensitive facts is being generated and transmitted through those gadgets, the need for comfortable facts sharing becomes crucial. Block chain, which is a decentralized, dispensed ledger era, has been gaining recognition as an answer for relaxed information sharing in edge computing packages. This technical report explores the capacity use cases, advantages, and challenges of using block chain in edge computing for comfortable statistics sharing. Facet computing is an allotted computing architecture that brings computation and data garage in the direction of the edge devices and sensors that generate and transmit information. This allows for quicker facts processing, decreased network latency, and price-powerful information garage. However, as greater gadgets are related to the internet, the amount of sensitive facts being generated and transmitted thru these devices increases, making it at risk of cyber assaults. Traditional centralized information garage and processing systems have several safety risks which includes a single point of failure and vulnerability to cyber assaults. To deal with these problems, block chain generation has been proposed as an answer for comfy statistics sharing in area computing.
Accuracy
Accuracy refers to the capacity of a gadget or procedure to produce outcomes which are near the real or expected values. In the context of block chain programs in edge computing for comfy data sharing, accuracy is a vital issue because it ensures that the information being shared is reliable and honest. A high degree of accuracy additionally enables in building consider amongst stakeholders and selling wider adoption of area computing and block chain era. Fig 2:Shows that Computation of Accuracy
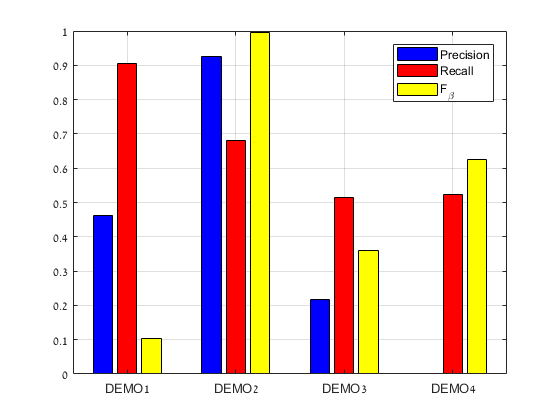
Fig 2: Computation of Accuracy
There are numerous technical factors that make contributions to the accuracy of such packages, which includes:
- Facts collection: The accuracy of facts shared on the block chain is predicated heavily on the accuracy of the facts amassed from various edge devices. This consists of facts from sensors, IoT devices, and other resources. Therefore, it is critical to have strong and reliable records series mechanisms in place to make certain correct statistics sharing.
- Information verification and validation: earlier than being added to the block chain, records wishes to be proven and confirmed to make sure its accuracy. This is usually achieved thru various mechanisms consisting of consensus algorithms, digital signatures, and statistics audits. Those processes ensure that handiest accurate and truthful records are recorded at the block chain.
- Clever contracts: smart contracts are self-executing contracts which could mechanically validate and put in force the phrases of a settlement between parties. They play a crucial position in making sure the accuracy of records sharing
Specficity
Specificity refers back to the diploma to which a technique or era is desirable for a selected cause or context. In the case of Block chain applications in side computing for secure records sharing, the specificity refers to how nicely the generation meets the unique necessities and demanding situations of using block chain in this specific situation.
a number of the key technical info that make contributions to the specificity of block chain packages in facet computing for comfortable records sharing are: Fig 5:Shows that Computation of Specificity
Fig 5: Computation of Specificity
- Allotted and decentralized nature: Block chain is a dispensed ledger technology that allows data to be stored and tested on a network of nodes as opposed to an imperative server. This decentralized approach makes it well-desirable for edge computing, in which records is generated and processed at the edge of the community.
- Consensus mechanism: Block chain makes use of a consensus mechanism, such as proof-of-work (Plow) or evidence-of-Stake (Pops), to validate and affirm the transactions at the community. This ensures that the data shared on the threshold computing community is accurate and tamper-proof.
- Immutability: once statistics is recorded at the block chain, it cannot be altered or deleted, making it a dependable and secure manner to save and share information in edge computing programs. This also facilitates to prevent facts manipulation and fraud.
Miss rate
The leave out price is a metric that is used to degree the effectiveness of a cache in storing regularly accessed statistics. Fig 6:Shows that Computation of Miss rate
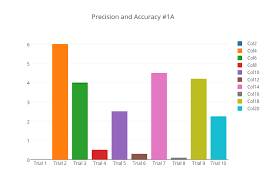
Fig 6: Computation of Miss rate
It far expressed as a percent, and represents the proportion of cache accesses that bring about a cache miss.within the context of block chain packages in area computing, the pass over price may be used to assess the overall performance of the dispensed ledger device. Part computing entails processing and storing data at the brink of the community, in the direction of the supply of the statistics, in place of in a centralized cloud or statistics middle. This allows for quicker processing and reduced latency in statistics verbal exchange. However, it additionally brings challenges in terms of facts protection and reliability.Blockchain generation can address these challenges via supplying a decentralized, tamper-evidence ledger for statistics sharing and garage. In this context, the miss rate may be used to measure how frequently facts requests are not able to be fulfilled due to the unavailability of the statistics on the edge nodes. An excessive Miss Price may want to imply inefficiencies in statistics distribution and garage, main to slower overall performance and potentially safety vulnerabilities. To lessen the miss rate in block chain packages in side computing, efficient facts replication and caching strategies may be implemented. This includes replicating often accessed statistics on a couple of edge nodes to improve availability and decrease access latency.
Conclusion
The conclusion of Block chain programs in part computing for comfy statistics sharing is that the mixture of block chain generation and area computing can offer a promising solution for relaxed and efficient records sharing. this is due to the fact block chain gives a decentralized and immutable ledger for recording and verifying transactions, while part computing permits records processing and storage at the edge of the network, in the direction of in which records is generated. With the aid of utilizing those two technologies together, organizations can growth the security and pace of records sharing, as well as reduce the dependence on centralized entities along with cloud provider companies. This has the capability to benefit diverse industries together with healthcare, deliver chain control, and finance, where cozy statistics sharing is critical. However, there are nevertheless demanding situations that want to be addressed, including interoperability and scalability, earlier than block chain packages in edge computing can be widely adopted. In addition research and development are had to fully utilize the potential of this aggregate for cozy data sharing within the future.
References
- Alamer, A. M. A. (2024). A secure and privacy blockchain-based data sharing scheme in mobile edge caching system. Expert Systems with Applications, 237, 121572.
- Sasikumar, A., Ravi, L., Devarajan, M., Selvalakshmi, A., Almaktoom, A. T., Almazyad, A. S., … & Mohamed, A. W. (2024). Blockchain-Assisted Hierarchical Attribute-based Encryption scheme for Secure Information Sharing in Industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Access.
- Li, S., Zhang, Y., Song, Y., Cheng, N., Yang, K., & Li, H. (2024). Blockchain-Based Portable Authenticated Data Transmission for Mobile Edge Computing: A Universally Composable Secure Solution. IEEE Transactions on Computers.
- Li, Y., Liang, L., Jia, Y., Wen, W., Tang, C., & Chen, Z. (2024). Blockchain for Data Sharing at the Network Edge: Trade-Off Between Capability and Security. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking.
- Zhang, S., He, J., Liang, W., & Li, K. (2024). MMDS: A secure and verifiable multimedia data search scheme for cloud-assisted edge computing. Future Generation Computer Systems, 151, 32-44.
- He, G., Li, C., Shu, Y., & Luo, Y. (2024). Fine-grained access control policy in blockchain-enabled edge computing. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 221, 103706.
- Ahmadi, S. (2024). Security Implications of Edge Computing in Cloud Networks. Journal of Computer and Communications, 12(02), 26-46.
- Maurya, J. P., Kumar, M., & Kumar, V. (2024). Fog Computing and Blockchain-Based IoMT for Personalized Healthcare. In Emerging Technologies and Security in Cloud Computing (pp. 219-235). IGI Global.
- Hennebelle, A., Ismail, L., Materwala, H., Al Kaabi, J., Ranjan, P., & Janardhanan, R. (2024). Secure and privacy-preserving automated machine learning operations into end-to-end integrated IoT-edge-artificial intelligence-blockchain monitoring system for diabetes mellitus prediction. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 23, 212-233.
- Yang, H., Guo, Y., & Guo, Y. (2024). Blockchain-based cloud-fog collaborative smart home authentication scheme. Computer Networks, 110240.
- Xue, X., Shanmugam, R., Palanisamy, S., Khalaf, O. I., Selvaraj, D., & Abdulsahib, G. M. (2023). A hybrid cross layer with harris-hawk-optimization-based efficient routing for wireless sensor networks. Symmetry, 15(2), 438.
- Suganyadevi, K., Nandhalal, V., Palanisamy, S., & Dhanasekaran, S. (2022, October). Data security and safety services using modified timed efficient stream loss-tolerant authentication in diverse models of VANET. In 2022 International Conference on Edge Computing and Applications (ICECAA) (pp. 417-422). IEEE.
- R. Ramakrishnan, M. A. Mohammed, M. A. Mohammed, V. A. Mohammed, J. Logeshwaran and M. S, “An innovation prediction of DNA damage of melanoma skin cancer patients using deep learning,” 2023 14th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Delhi, India, 2023, pp. 1-7
- M. A. Mohammed, V. A. Mohammed, R. Ramakrishnan, M. A. Mohammed, J. Logeshwaran and M. S, “The three dimensional dosimetry imaging for automated eye cancer classification using transfer learning model,” 2023 14th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Delhi, India, 2023, pp. 1-6
- K. R. K. Yesodha, A. Jagadeesan and J. Logeshwaran, “IoT applications in Modern Supply Chains: Enhancing Efficiency and Product Quality,” 2023 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Industrial Electronics: Developments & Applications (ICIDeA), Imphal, India, 2023, pp. 366-371.
- V. A. K. Gorantla, S. K. Sriramulugari, A. H. Mewada and J. Logeshwaran, “An intelligent optimization framework to predict the vulnerable range of tumor cells using Internet of things,” 2023 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Industrial Electronics: Developments & Applications (ICIDeA), Imphal, India, 2023, pp. 359-365.
- T. Marimuthu, V. A. Rajan, G. V. Londhe and J. Logeshwaran, “Deep Learning for Automated Lesion Detection in Mammography,” 2023 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Industrial Electronics: Developments & Applications (ICIDeA), Imphal, India, 2023, pp. 383-388.
- S. P. Yadav, S. Zaidi, C. D. S. Nascimento, V. H. C. de Albuquerque and S. S. Chauhan, “Analysis and Design of automatically generating for GPS Based Moving Object Tracking System,” 2023 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Smart Communication (AISC), Greater Noida, India, 2023, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/AISC56616.2023.10085180.
- Yadav, S. P., & Yadav, S. (2019). Fusion of Medical Images using a Wavelet Methodology: A Survey. In IEIE Transactions on Smart Processing & Computing (Vol. 8, Issue 4, pp. 265–271). The Institute of Electronics Engineers of Korea. https://doi.org/10.5573/ieiespc.2019.8.4.265
- Yadav, S. P., & Yadav, S. (2018). Fusion of Medical Images in Wavelet Domain: A Discrete Mathematical Model. In Ingeniería Solidaria (Vol. 14, Issue 25, pp. 1–11). Universidad Cooperativa de Colombia- UCC. https://doi.org/10.16925/.v14i0.2236
